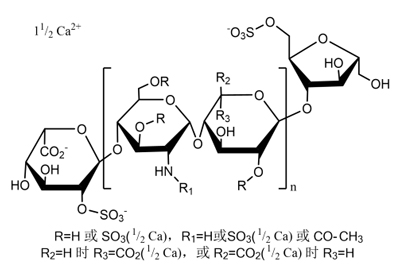
Nadroparin Calcium
CAS No.: 37270-89-6 (Low molecular weight heparin)
Specification
| Nadroparin calcium | ||
| Source | Intestinal mucosa of pigs | |
| Quality standard |
EP |
|
| characters | Appearance | white or almost white; hygroscopic powder |
| solubility | freely soluble in water | |
| identification |
The 13C NMR spectrum obtained is similar to that obtained with the appropriate specific nadroparin calcium CRS |
|
|
Anti- factor Xa activity/ anti-factor IIa : 2.5-4.0 |
||
|
Mw : 3600 -5000Da, M≤2000 : NMT 15%, M2000-8000:75%-95%, M2000-4000:35%-55% |
||
| It complies with the test for calcium | ||
| Appearance of solution |
The solution is not more opalescent than reference suspension II and not more intensely coloured than reference solution Y5 |
|
| Ethanol |
≤1.0% |
|
| pH |
5.5-8.0 |
|
| N-NO groups |
≤ 0.25 ppm |
|
| Free sulfates |
≤ 0.5% |
|
| Molar ratio of Sulfate carboxylate | ≥1.8 | |
| Nitrogen |
1.5 %-2.5 % (on the dried basis) |
|
| calcium |
9.5% -11.5% (on the dried basis) |
|
| Loss on drying |
NMT 10.0% |
|
| Bacterial endotoxins |
<0.01EU/IU |
|
| Assay |
95-130 IU/mg (on the dried basis) |
|
Indications
In surgery, it is used for the prevention of venous thromboembolic disease in cases of medium-high or high risk of venous thrombosis.
Treatment of deep vein thrombosis that has developed.
Combined with aspirin for the treatment of unstable angina pectoris and acute phase of non-Q-wave myocardial infarction.
Prevention of blood clot formation during cardiopulmonary bypass during hemodialysis.
CAS No.: 679809-58-6 (Low molecular weight heparin)
CAS No. : 80449-31-6 (Trypsin Inhibitor )